Conductive deafness and sensorineural deafness are two of the more common types of deafness. These two types of deafness also have some differences in the effectiveness of hearing aids. Generally speaking, the effects of conductive deafness are better than those Patients with phonological deafness.
Everyone knows that our ears are mainly composed of the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. The main function of the outer and middle ears is to transmit sound. The sound is transmitted to the inner ear through the outer and middle ears. The cochlea in the inner ear serves as the main auditory sensory organ to process sound signals. Therefore, conductive deafness is generally caused by problems in the outer and middle ears, which prevents sound signals from being transmitted to the inner ear, such as perforation of the tympanic membrane, otitis media, and obstruction of the diaphragm. For patients with conductive deafness, their inner ear and auditory nerve functions are usually normal. At this time, we only need to solve the problem of sound transmission, and generally we can solve the patient’s hearing problem.
For conductive deafness, we can treat it with drugs or surgery, such as repairing damaged eardrums, removing foreign bodies from blocked ear canals, and treating otitis media with drugs. If conductive deafness cannot be cured by medication or surgery, then the patient’s hearing compensation through optional hearing aids is a good solution. Hearing aids amplify the sound to help us pass sound through the middle ear, and then the sound signal is processed by the normally functioning inner ear, thereby improving the problem of hearing loss. Because the inner ear function of patients with conductive hearing loss is generally normal, the effect of optional hearing aids is much better than that of patients with neurological deafness.
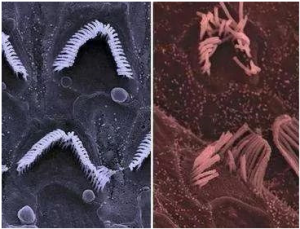
After talking about conductive deafness, let’s talk about sensorineural deafness. Nearly 90% of the patients we contacted are sensorineural deafness. This hearing loss is caused by damage to the cochlea or auditory nerve. The more common ones are caused by noise, and the natural aging of the human body. Once the sound hair cells in the cochlea are damaged, it is an irreversible damage. The current level of medical technology cannot repair them, and the human body cannot regenerate the hair cells to replace the damaged hair cells. We can look at normal hair cells and damaged hair cells in the following figure:
Healthy hair cells (left) and damaged hair cells (right)
In summary, sensorineural deafness is different from conductive deafness. Sensorineural deafness is often accompanied by the problem of distortion of the auditory system. Many of these patients will hear what they hear, but they can’t hear well, which means they can’t understand the content of the sound. At this time, even with a hearing aid to amplify the sound, the patient can hear the sound but cannot fully understand the meaning of the sound. This requires that after selecting a hearing aid, the patient must restore his ability to distinguish from speech through continuous adaptation and exercise, and exercise can still improve the effect to a certain extent. Don’t give up wearing hearing aids because hearing sensory hearing loss is not ideal. That will only make your hearing loss worse, and your speech discrimination ability worse. In the end, the earlier the hearing loss is, the better the hearing aid will be.
The article comes from the Internet. If there is any infringement, please contact service@jhhearingaids.com to delete it.